Reliable weather monitoring supports safer operations and smarter planning. Modern projects in farming, aviation, renewable energy, and urban infrastructure depend on integrated meteorological instruments and high-precision weather sensors. Because monitoring goals vary, the required environmental monitoring equipment also differs.
In this article, we review 18 types of weather instruments, their principles, industry uses, and practical selection tips.
Why Weather Instruments Matter in Industrial & Government Projects
Weather instruments play a vital role in maintaining safety, meeting regulations, and protecting assets. They deliver real-time data for remote monitoring, trigger automation responses, and strengthen prediction and alert capabilities. Integrated with an IoT weather station, consistent data accuracy becomes the backbone of smart management systems.

18 Types of Weather Instruments and Their Uses
Understanding the role of equipment and the data it collects is crucial when building a reliable monitoring system. Different environments, accuracy requirements, and application goals determine which instruments should be deployed and how they work together within a complete meteorological monitoring network. From basic observations to automated decision support, each sensor provides a specific level of environmental information.
Below is a list of commonly used 18 types of weather instruments and meteorological sensors, along with their main functions and typical industry applications, to help you select the appropriate technology based on your project needs.
Thermometer
A thermometer measures ambient air temperature and is one of the core inputs in weather monitoring networks. It is widely used for HVAC control, agricultural production, laboratory environments, and process protection where stable thermal data is required.
Typical parameters
Measurement range: −40 to +80 °C (customizable)
Accuracy: ±0.1 to ±0.5 °C
Output: RS485 / SDI-12 / analog
Barometer
Barometers monitor atmospheric pressure and serve as vital tools for weather forecasting, flight altitude correction, and automated control systems. Real-time pressure trend analysis aids in short-term weather forecasting, enhancing safety and decision-making efficiency.
Typical parameters
Range: 300–1100 hPa
Accuracy: ±0.1–0.5 hPa
Long-term stability: ≤1 hPa/year
Hygrometer
Hygrometers are used for precise measurement of air relative humidity, serving as essential tools for environmental control and process management. They are widely employed in humidity-sensitive environments such as warehouses, pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities, cleanrooms, and greenhouses. These instruments facilitate real-time monitoring and maintenance of optimal humidity levels, thereby ensuring product quality, process stability, and personnel safety.
Typical parameters
Range: 0–100 %RH
Accuracy: ±2–3 %RH
Response time: ≤10 s
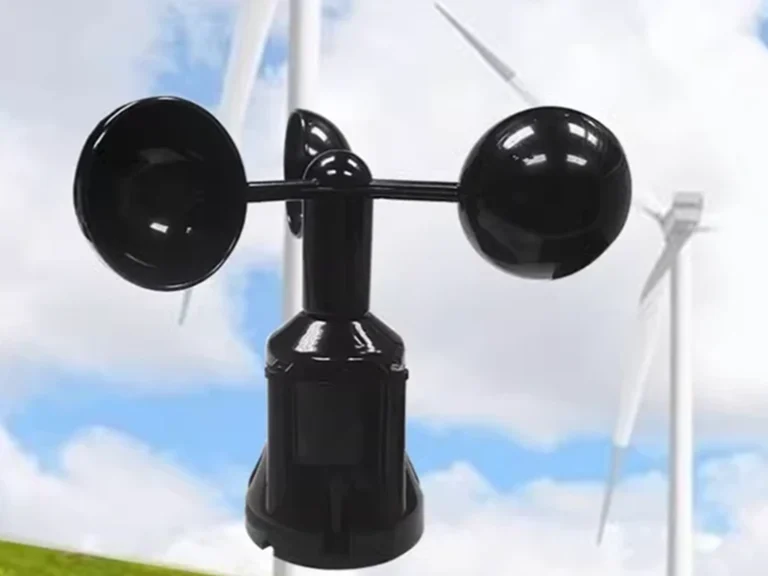
مقياس شدة الريح
An anemometer measures wind speed for operational safety and efficiency. It is widely deployed in wind farms, ports, construction sites, and airports. Please see details: ما هو مقياس شدة الريح؟ فهم الجهاز الذي يقيس الرياح
Typical parameters
Range: 0–60 m/s or higher
Starting threshold: ≤0.3 m/s
Accuracy: ±(0.3 m/s or 3%)

Wind Vane
A wind vane determines wind direction, supporting runway management, crane operation, and dispersion analysis.
Typical parameters
Range: 0–360°
Accuracy: ±3°
Resolution: 1°

مقياس المطر
Rain gauges record precipitation for hydrology studies, flood prevention, agricultural planning, and municipal drainage systems.
Typical parameters
Resolution: 0.1–0.5 mm
Accuracy: ±2–3%
Outpt: pulse / RS485
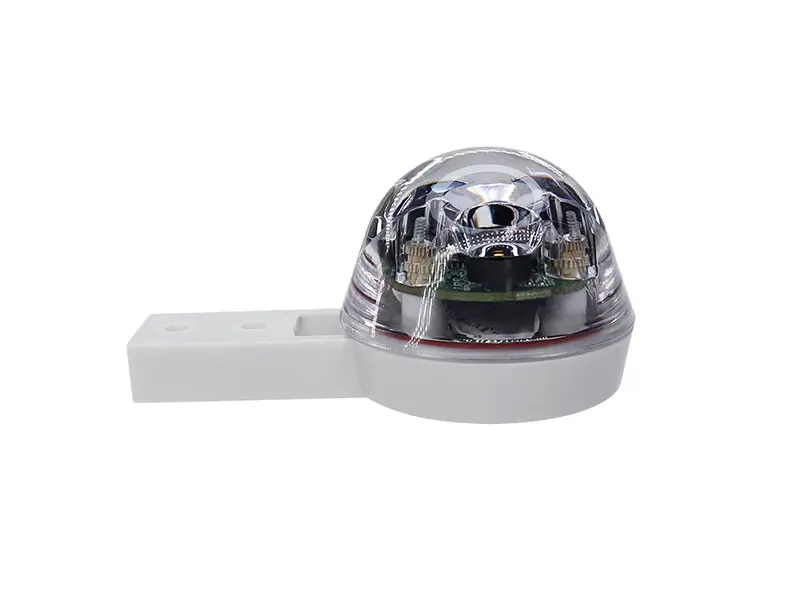

Pyranometer
A pyranometer measures global solar radiation and is fundamental for PV performance analysis and energy yield forecasting.
Typical parameters
Range: 0–2000 W/m²
Spectral range: 285–2800 nm
Accuracy: secondary standard or better

Sunshine Recorder
This device logs sunshine duration, supporting agriculture, tourism studies, and solar resource evaluation.
Typical parameters
Threshold: ~120 W/m²
Resolution: 1 min
Annual deviation: <3%
Evaporimeter
An evaporimeter measures evaporation rate, providing guidance for irrigation management and water resource planning.
Typical parameters
Range: 0–20 mm/day typical
Resolution: 0.1 mm
Accuracy: ±2%
Ceilometer
A ceilometer uses laser technology to determine cloud base height, a critical metric for aviation safety and automated runway decisions.
Typical parameters
Range: up to 7–15 km
Resolution: 5–10 m
Eye safety: Class 1
مستشعر الرؤية
Visibility sensors evaluate atmospheric transparency for highways, marine navigation, and airport operations.
Typical parameters
Range: 10 m–50 km
Accuracy: ±10%
Measurement principle: forward scatter

Snow Gauge
A snow gauge measures snowfall and water equivalent, supporting hydropower forecasting and winter road management.
Typical parameters
Range: project dependent
Resolution: 0.1 mm water equivalent
Operating temp: down to −40 °C

Soil Temperature Sensor
This sensor monitors subsurface temperature for crop modeling, ecological research, and infrastructure protection.
Typical parameters
Range: −40 to +80 °C
Accuracy: ±0.2 °C
Probe depth: customizable
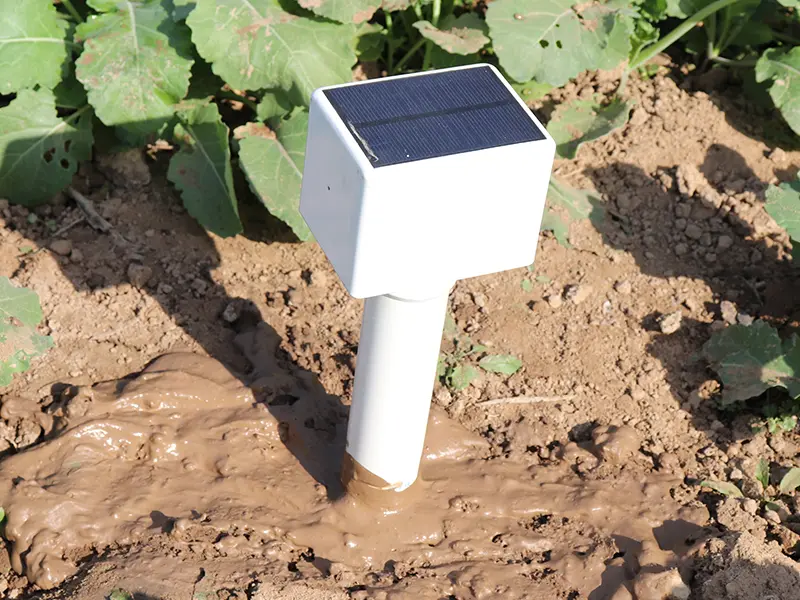

Soil Moisture Sensor
Used in precision agriculture, soil moisture sensors guide irrigation scheduling and water conservation.
Typical parameters
Range: 0–100% VWC
Accuracy: ±2–3%
Output: digital / analog
Leaf Wetness Sensor
Leaf wetness data supports plant disease modeling and spray decision systems in orchards and greenhouses.
Typical parameters
Detection: wet/dry or resistance value
Accuracy: event-based
Operating temp: −40 to +60 °C
UV Sensor
UV sensors monitor ultraviolet radiation for public safety, environmental research, and material durability studies.
Typical parameters
Spectral band: UVA/UVB selectable
Range: 0–200 W/m² typical
Accuracy: ±5%

Weather Radar
Weather radar provides large-scale precipitation and storm tracking. It is vital for disaster prevention and regional forecasting.
Typical parameters
Coverage: tens to hundreds of km
Scan cycle: minutes
Output: reflectivity / velocity
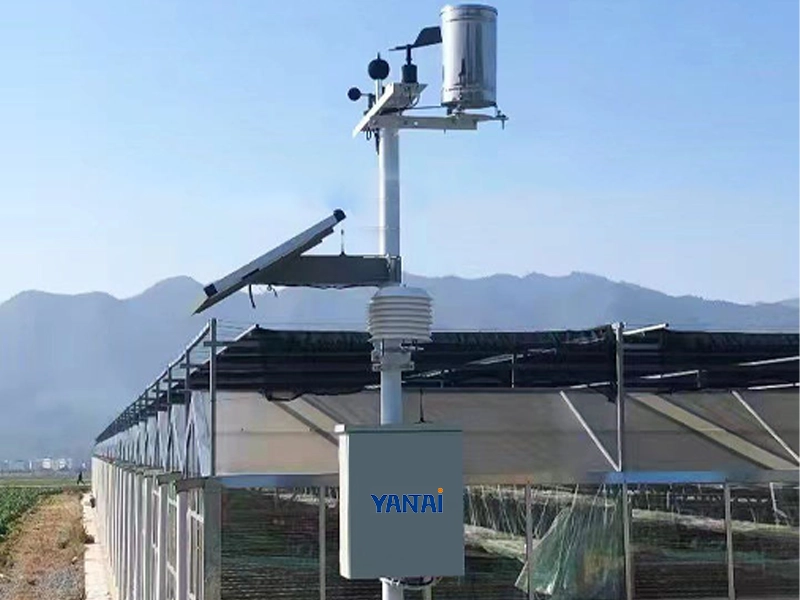
Automatic Weather Station (AWS)
An Automatic Weather Station integrates multiple sensors, data loggers, communication modules, and power systems. It enables unattended, real-time monitoring and seamless platform integration.
Typical parameters
Multi-parameter inputs: scalable
Communication: 4G / satellite / Ethernet
Power: solar + battery options

How to Choose the Right Meteorological Monitoring Instruments
When selecting meteorological monitoring instruments and environmental monitoring equipment, in addition to checking specifications, you should also consider reliability, integration, and return on investment. Suitable instruments can ensure data accuracy, support automated systems, and reduce operational risks. Here are some key selection points for your reference.
Key Selection Criteria for Procurement
| Selection Factor | What to Check |
|---|---|
| Measurement Parameters | Identify which variables are needed: temperature, humidity, wind, pressure, rainfall, solar radiation, etc. |
| Accuracy Requirements | Review sensor accuracy, resolution, repeatability. |
| Installation Environment | Assess outdoor exposure, indoor conditions, temperature extremes, dust, humidity, or salt spray. |
| Communication Protocol | Confirm compatibility with RS485, SDI-12, Modbus, LoRa, 4G, or Ethernet. |
| مزود الطاقة | Decide between mains, battery, or solar options; check autonomy for remote locations. |
| Calibration & Maintenance | Check ease of calibration, remote diagnostics, and service availability. |
Integrated Weather Monitoring Solutions
For industrial, agricultural, and aviation projects, buying single meteorological instruments is no longer enough. Modern operations demand integrated weather monitoring solutions that combine multiple sensors, data management, and platform connectivity to deliver accurate, real-time insights.
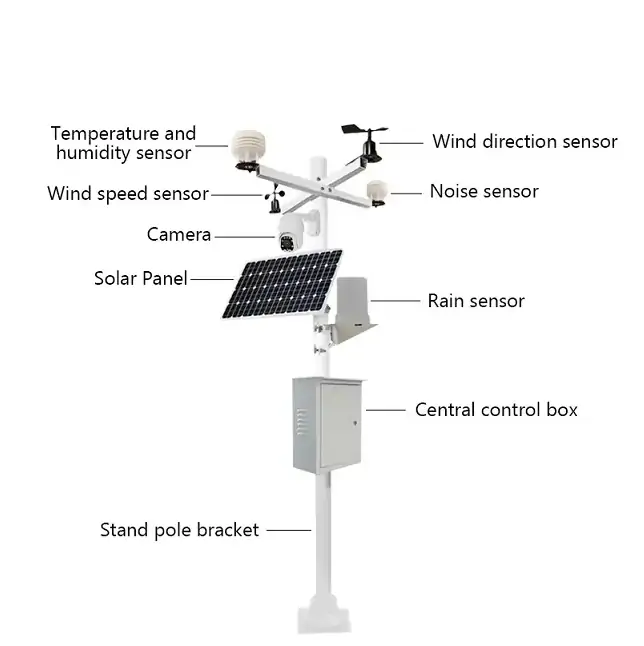

Multi-Sensor Integration
Our solutions combine weather sensors for temperature, humidity, wind, pressure, precipitation, solar radiation, and more into a single system. Multi-sensor setups provide comprehensive environmental monitoring, ensuring no critical parameter is missed.
Data Acquisition Units
All sensors feed into robust data acquisition units, which collect, synchronize, and preprocess the data. This ensures high data accuracy, reduces transmission errors, and allows for seamless integration with software platforms.
Software Platform
The collected data is processed through a centralized software platform, offering real-time visualization, historical data analysis, and configurable alerts. Decision-makers can quickly monitor conditions and optimize operations based on accurate environmental insights.
Cloud-Based Transmission
Our systems support cloud transmission, enabling remote monitoring and centralized management. Teams can access data anytime, anywhere, improving operational efficiency and responsiveness.
API Integration with SCADA / EMS
For industrial and energy applications, our solutions provide APIs for seamless connection to SCADA and EMS systems. This allows weather data to drive automated control, safety interlocks, and predictive maintenance across operational platforms.
Industry Applications of Meteorological Instruments
Meteorological instruments and sensors are widely deployed across multiple sectors. Integrating these devices into operational workflows enhances safety, efficiency, and decision-making capabilities.
Agriculture and Smart Farming
Weather monitoring enables precision irrigation, crop modeling, and disease prevention. Soil moisture, temperature, rainfall, and solar radiation sensors help farmers optimize water usage, boost yields, and reduce resource waste.
Airports and Aviation
High-precision meteorological instruments provide airports with real-time wind speed, wind direction, visibility, and cloud height data. This ensures flight safety, runway management, and automated controls while meeting aviation regulatory requirements.
Renewable Energy
Wind power and solar projects rely on meteorological sensors to monitor wind speed, temperature, and solar radiation. This optimizes energy production, protects equipment, enables predictive maintenance, and improves operational efficiency.
Marine and Ports
Ports and terminals utilize environmental monitoring equipment to track wind, temperature, humidity, and visibility, ensuring navigational safety, preventing accidents, and protecting personnel.
Highways and Transportation
Meteorological instruments provide data support for road safety by monitoring visibility, precipitation, wind, and temperature. They integrate with traffic management systems to enable timely warnings and maintenance decisions.
الرصد البيئي
Cities, industrial zones, and research institutions rely on meteorological instruments for long-term climate monitoring, air quality assessment, and disaster preparedness, ensuring regulatory compliance and supporting sustainable planning.
مواقع الإنشاءات
Construction sites utilize meteorological sensors to monitor wind speed, precipitation, and temperature, ensuring site safety, equipment protection, and minimizing weather-related delays.
Request a Weather Monitoring Solution
Whether you are managing agriculture, airports, ports, or industrial sites, مستشعر يان تاي provides reliable Weather Instruments and integrated weather monitoring solutions tailored to your project needs. Our experienced engineers support system design, sensor selection, and deployment planning to ensure accurate, real-time environmental data for safe and efficient operations. Contact us Today for a solution.