With the growing trend of refined management and intelligent monitoring, anemometers are widely used in meteorological monitoring, agriculture, industry, and other fields. As technology evolves, anemometers have advanced from traditional models to high-precision ultrasonic anemometers. So, how much do you know about anemometers? What is an anemometer used for? Anemometer, how does it work?
This article will give you the answers!

What is an anemometer used for?
The main function of an anemometer is to measure the flow speed of air—that is, wind speed. In some multifunctional devices, it can also be integrated with a wind direction sensor to become a wind speed and direction sensor, capable of simultaneously monitoring both wind speed and direction. These types of sensors are widely used in weather stations and environmental monitoring sites, wind farms, smart agriculture and greenhouse management, high-altitude work safety monitoring, construction sites, and crane operation monitoring.
In these environments, accurate wind speed data is essential for safety control and environmental assessment.

Anemometer, how does it work?
So how does an anemometer work? Different anemometers operate based on different principles. Here, I will mainly introduce the two most common types: mechanical anemometers and ultrasonic anemometers.
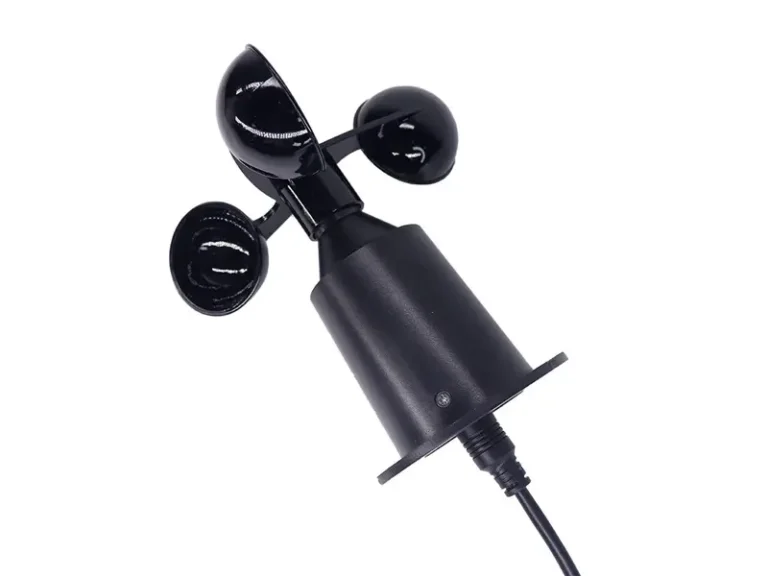
1. Working principle of mechanical anemometers
The mechanical anemometers usually adopt a cup or impeller design. When wind passes through, the wind force drives the rotor to rotate, and the rotational speed is proportional to the wind speed. The internal sensing system of the instrument converts the rotation frequency into wind speed data.

2. Working principle of ultrasonic anemometers
Ultrasonic anemometers are modern devices without mechanical components, offering fast response and high accuracy. They operate by emitting and receiving ultrasonic signals, using the influence of wind on sound wave propagation time to calculate wind speed and direction.
Simply put, wind flowing in the direction of ultrasonic propagation accelerates the wave speed, while wind flowing against it slows it down. By comparing the time differences in multiple directions, the device can precisely calculate wind speed and direction data. This is currently one of the most advanced wind speed and direction sensor technologies.
So, if you’re looking for a more accurate anemometer, you can choose an ultrasonic anemometer. If you’re looking for a more cost-effective option, a mechanical anemometer may be more suitable.

Applications of anemometers
With the popularization of automated monitoring and data-driven decision-making, anemometers have been widely applied across multiple industries. High-precision devices, such as ultrasonic anemometers, play important roles in the following fields:
Meteorological monitoring: For weather forecasting, wind warnings, and climate research.
Wind power generation: To monitor wind speed changes and guide turbine startup, shutdown, and power control.
Agriculture: To help farmers manage greenhouse ventilation, pesticide spraying timing, and more.
Transportation: For safety monitoring at viaducts, airports, and similar locations.

Scientific research and engineering construction: To provide wind speed data support for high-rise buildings and large bridge projects.
We hope this article helps you choose the right wind speed measurement device based on your needs. Whether you opt for the traditional mechanical type or the high-precision ultrasonic anemometer, proper use of anemometers and wind speed & direction sensors can significantly enhance your environmental monitoring and safety management capabilities.
If you need, you are welcome to come to us at any time!