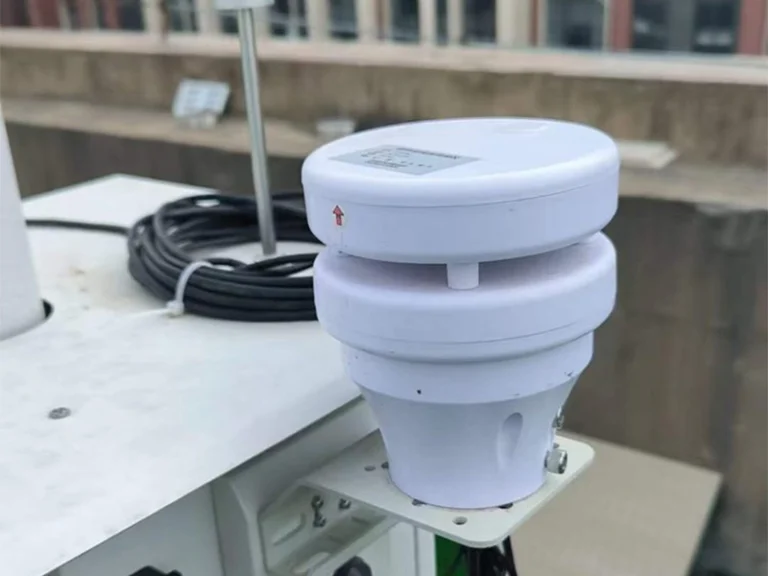
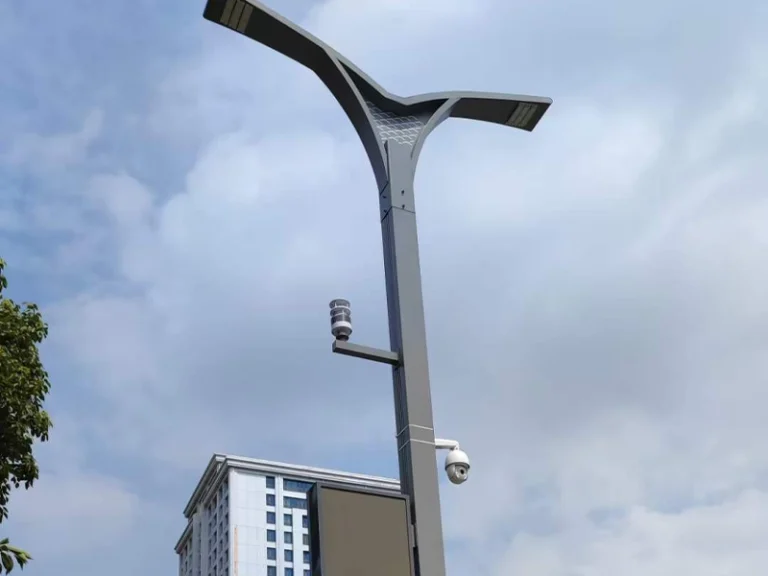
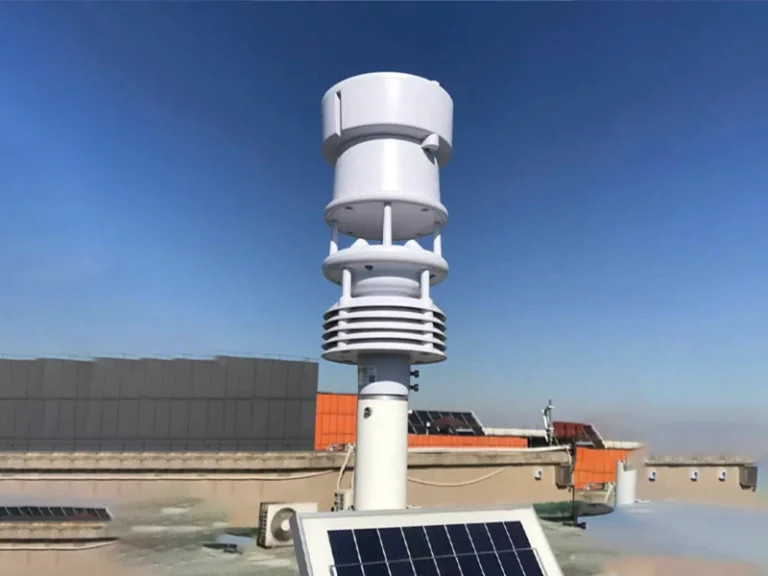
In modern smart agriculture systems, agricultural production is gradually shifting from “experience-driven” to “data-driven.” To achieve precise management of crop growth environments, soil conditions, and water-fertilizer regimes, various agricultural sensors are widely deployed across fields, greenhouses, orchards, and seedling nurseries. These sensors cover multiple dimensions—from environmental parameters to soil physicochemical indicators—providing continuous, reliable foundational data support for agricultural production.
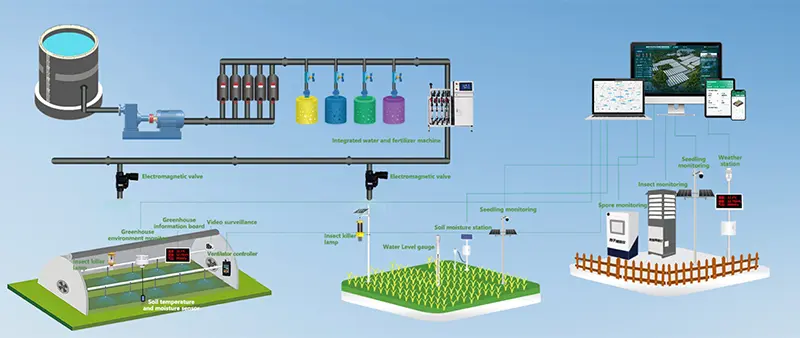
Based on monitoring targets and application scenarios, agricultural sensors can be categorized into air environment sensors, soil monitoring sensors, water and fertilizer management sensors, and crop growth parameter monitoring sensors. Different sensor types work in tandem to form a comprehensive agricultural environmental sensing network, serving as the essential foundation for precision irrigation, scientific fertilization, and crop growth assessment.
What Are Agriculture Sensors and Why Do They Matter in Modern Farming
Agricultural sensors are smart tools that help farmers “understand” their land. They automatically monitor soil moisture, fertility, and pH levels around the clock, along with field temperature and light intensity, transforming crop growth environments into real-time data that’s easy to grasp at a glance. From now on, watering and fertilizing no longer rely on guesswork, making cultivation management more precise and hassle-free—suitable for greenhouses, orchards, and open fields alike.
Why Agriculture Sensors Matter in Modern Farming
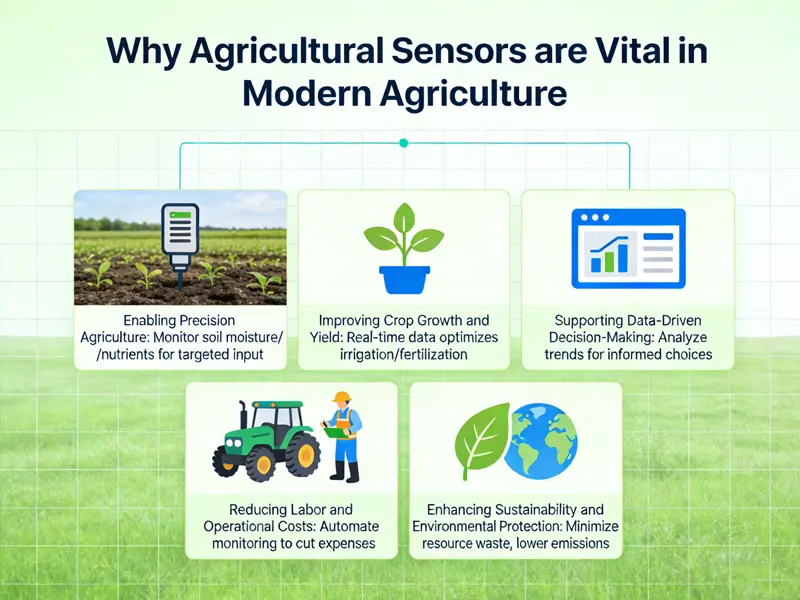
In modern farming, efficiency, sustainability, and productivity are more important than ever. Agriculture sensors play a critical role by:
- Enable Precision Agriculture
Say goodbye to flood irrigation. Sensors deliver targeted watering and fertilization—exactly where needed—saving money and resources. - Improve Crop Growth and Yield
Constant sensor monitoring ensures crops thrive in optimal conditions, reducing disease and stress for healthier growth and higher yields. - Support Data-Driven Decision Making
Real-time and historical sensor data provide valuable insights for irrigation scheduling, fertilization planning, and climate control. - Reduce Labor and Operational Costs
Sensors monitor fields 24/7, drastically cutting the need for manual inspections. Save time, effort, and expenses. - Enhance Sustainability and Environmental Protection
Precision inputs prevent over-irrigation and over-fertilization, protecting soil and water sources while making farming By preventing over-irrigation and excessive fertilizer use, sensors help protect soil quality and water resources.
As agriculture continues to evolve toward digital and intelligent systems, agricultural sensors have become a foundational component of smart farming, precision agriculture, and IoT-based agricultural solutions. In the following sections, different types of agriculture sensors and their specific applications will be introduced to help clarify how they are used in real-world farming scenarios.
List of agriculture sensors
Agriculture sensors are used to monitor environmental, soil, and crop-related parameters, helping farmers make data-driven decisions throughout the growing cycle. Below is a comprehensive list of commonly used agriculture sensors and their roles in agricultural applications.
1. Air Temperature Sensor
Air temperature sensors measure ambient temperature around crops. Temperature is a key factor influencing plant metabolism, growth rate, flowering, and yield. These sensors are widely used in open fields, greenhouses, and nurseries to support climate control, frost prevention, and crop growth optimization.
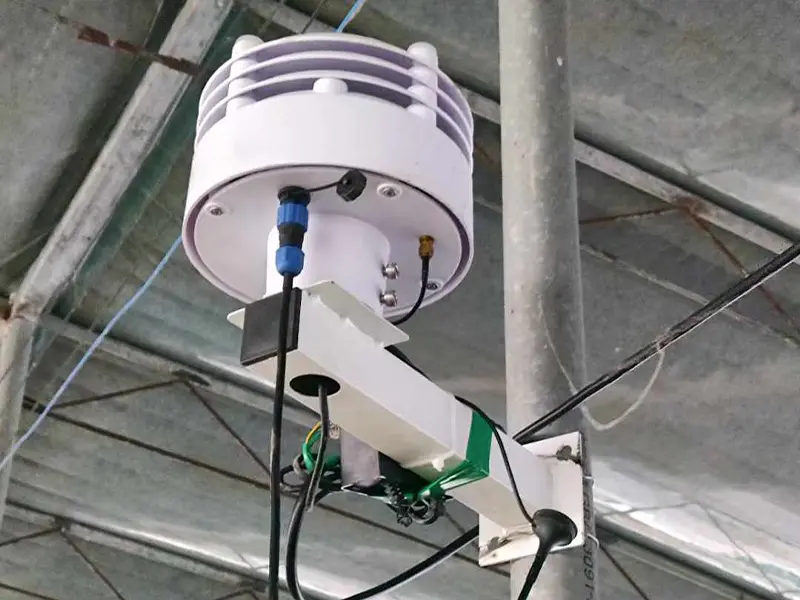

2. Air Humidity Sensor
Air humidity sensors monitor the moisture content in the air. Maintaining appropriate humidity levels helps prevent plant diseases, reduce transpiration stress, and improve overall crop health. They are commonly integrated into greenhouse climate control and weather monitoring systems.
3. Soil Moisture Sensor
Soil moisture sensors measure the water content in the soil, enabling precise irrigation management. By providing real-time data, these sensors help avoid over-irrigation or water stress, improving water-use efficiency and supporting healthy root development.
4. Soil Temperature Sensor
Soil temperature sensors track temperature conditions in the root zone. Soil temperature affects seed germination, nutrient uptake, and microbial activity. These sensors are essential for planting decisions, irrigation planning, and seasonal crop management.

5. Soil pH Sensor
Soil pH sensors measure the acidity or alkalinity of the soil. Since soil pH directly influences nutrient availability, continuous monitoring helps farmers adjust fertilization strategies and maintain optimal growing conditions for different crops.
6. Soil Electrical Conductivity (EC) Sensor
Soil EC sensors measure the soil’s ability to conduct electrical current, which is closely related to salinity and nutrient concentration. These sensors are commonly used to evaluate soil fertility, detect salt buildup, and manage fertilizer application more effectively.
7. Light Intensity Sensor
Light intensity sensors measure solar radiation or photosynthetically active radiation (PAR). Light availability directly affects photosynthesis and plant development. These sensors are widely used in greenhouses and controlled-environment agriculture to optimize lighting and shading strategies.
8. Rainfall Sensor
Rainfall sensors measure precipitation levels and distribution. They help farmers evaluate natural water input, adjust irrigation schedules, and manage drainage systems, especially in large-scale field farming and precision agriculture applications.
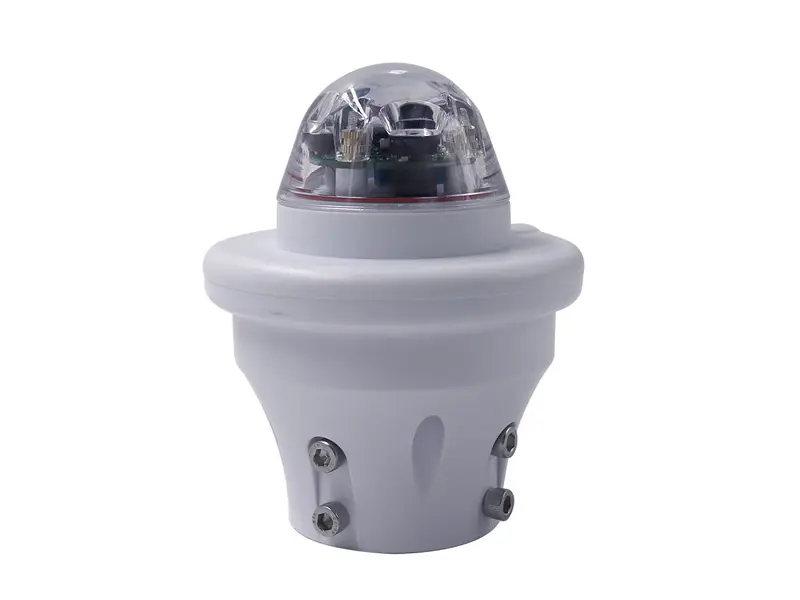

9. Wind Speed and Direction Sensor
Wind sensors monitor airflow conditions in agricultural environments. Wind data is important for spray drift control, greenhouse ventilation management, and assessing crop stress caused by strong winds or storms.
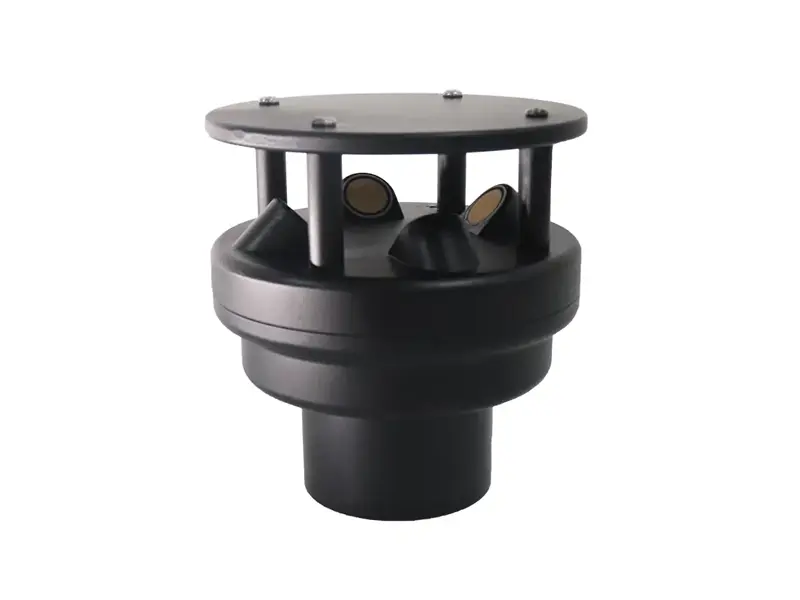

10. CO₂ Sensor
CO₂ sensors measure carbon dioxide concentration in the air. In greenhouse agriculture, CO₂ enrichment is often used to enhance photosynthesis. Monitoring CO₂ levels ensures optimal plant growth while maintaining safe and efficient environmental control.
11. Leaf Wetness Sensor
Leaf wetness sensors detect moisture on plant surfaces. They are primarily used for disease prediction and early warning systems, helping farmers reduce crop losses caused by fungal and bacterial infections.
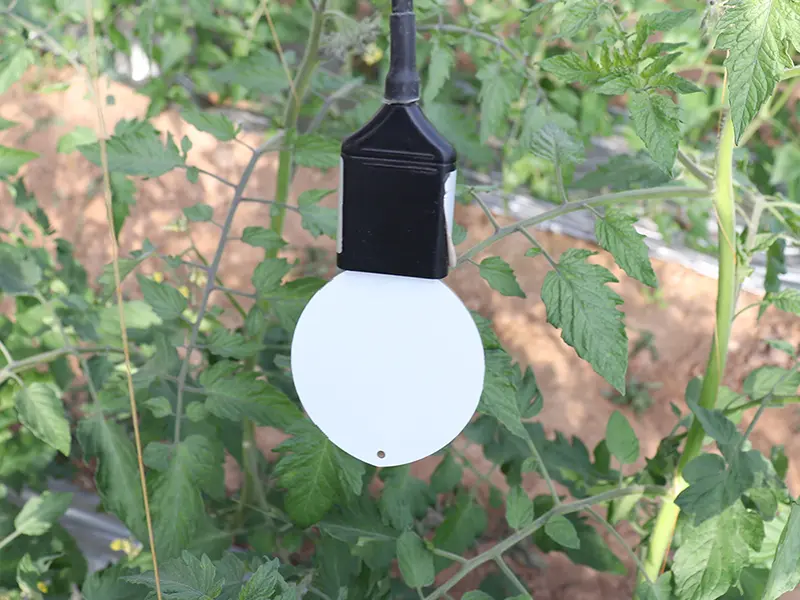

12. Water Quality Sensor
Water quality sensors monitor parameters such as pH, EC, temperature, and dissolved solids in irrigation water or nutrient solutions. These sensors are critical in fertigation systems and hydroponic agriculture to ensure consistent and safe water supply.
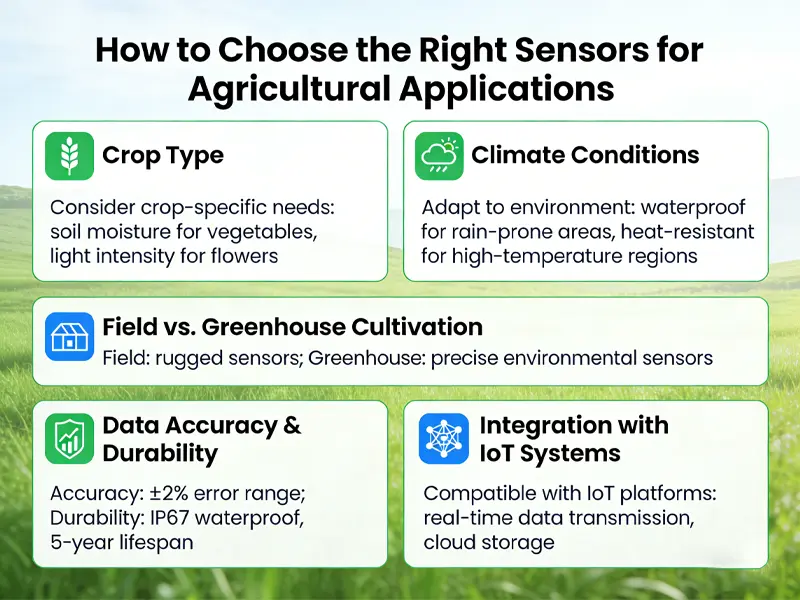
How to Choose the Right Sensors for Your Agriculture Application
Choosing the right agriculture sensors starts with understanding your specific farming conditions and operational goals. Different crops, environments, and management systems require different sensing solutions.
Crop Type
Different crops have unique environmental and soil requirements. For example, vegetables, fruits, and cereals respond differently to temperature, moisture, pH, and nutrient levels. Selecting sensors that match crop-specific monitoring needs helps optimize growth and yield.
Climate Conditions
Local climate plays a major role in sensor selection. Sensors used in high-humidity, high-temperature, or extreme weather environments must offer strong environmental resistance and long-term stability to ensure reliable data collection.
Open Field vs. Greenhouse
Open-field agriculture requires sensors with robust weatherproof designs and wide measurement ranges, while greenhouse applications focus more on high accuracy and real-time environmental control. Choosing sensors designed for your farming environment improves performance and system reliability.
Data Accuracy and Durability
Accurate data is essential for precision farming. High-quality sensors with stable calibration, low drift, and durable construction reduce maintenance costs and ensure consistent long-term monitoring.
Integration with IoT Systems
Modern agriculture relies on connected systems. Sensors that support standard communication protocols such as RS485, SDI-12, or Modbus integrate easily with IoT platforms, data loggers, and smart farming systems, enabling centralized data analysis and automation.
Conclusión
Agriculture sensors have become an essential foundation of modern, data-driven farming. From monitoring soil conditions and climate factors to supporting precision irrigation and fertilization, the right sensors enable farmers to make smarter decisions and improve productivity. By understanding different sensor types and carefully selecting solutions based on crop requirements, environmental conditions, and system compatibility, agricultural operations can achieve greater efficiency and sustainability. Partnering with a professional agriculture sensor manufacturer further ensures long-term accuracy, reliability, and scalable support for future smart farming applications.






