Choosing the right anemometer types is the decisive factor in wind measurement accuracy. While environmental variables matter, most data inconsistencies and control system errors are caused by a fundamental mismatch between the sensor technology and its application.
With so many anemometer types available on the market, including cup anemometers, propeller anemometers, ultrasonic anemometers, and more, each design offers distinct advantages and limitations. Different application scenarios place very different demands on measurement stability, accuracy, response speed, and environmental adaptability.
Choosing the right solution is therefore not about selecting the most expensive instrument, but about matching the anemometer type to your specific operating conditions and performance requirements. This article analyzes the characteristics and typical applications of major anemometer types from a practical perspective, helping you identify a clear and reliable selection path.

Seven Different Anemometer Types
Each category below is presented in the following order: principle → characteristics → applications → advantages and disadvantages, making it easy to compare and select the most suitable option.
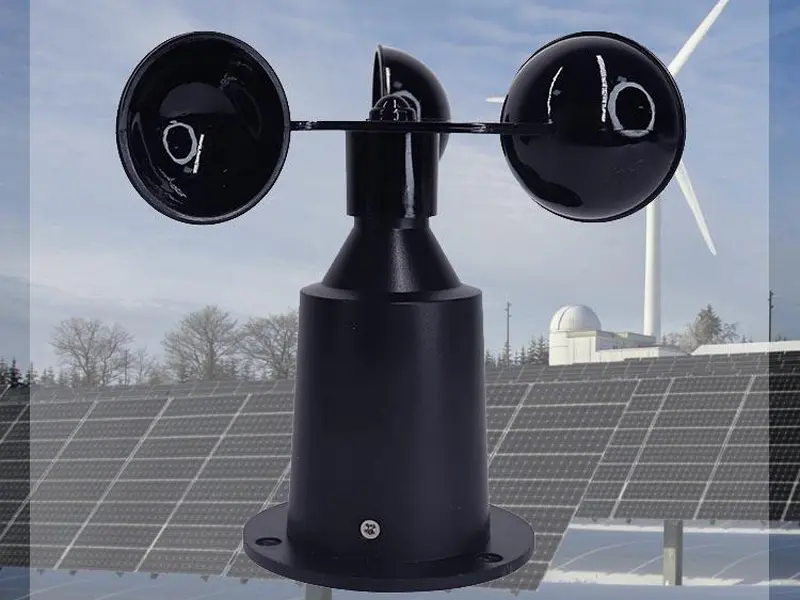
1. Cup Anemometer
Working Principle: Wind propels the cups to rotate, with rotational speed proportional to wind speed.
Tính năng
- Accuracy: Moderate
- Range: Low-to-medium to medium-to-high wind speeds
- Response Speed: Average
- Durability: High
- Cost: Low
Đơn đăng ký
- Weather stations
- Giám sát môi trường
- Khí tượng nông nghiệp
- General long-term field monitoring
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simple structure, stable, and reliable | Low sensitivity at low wind speeds |
| Low cost, easy maintenance | Subject to mechanical wear |
| High industry acceptance | Requires periodic calibration |
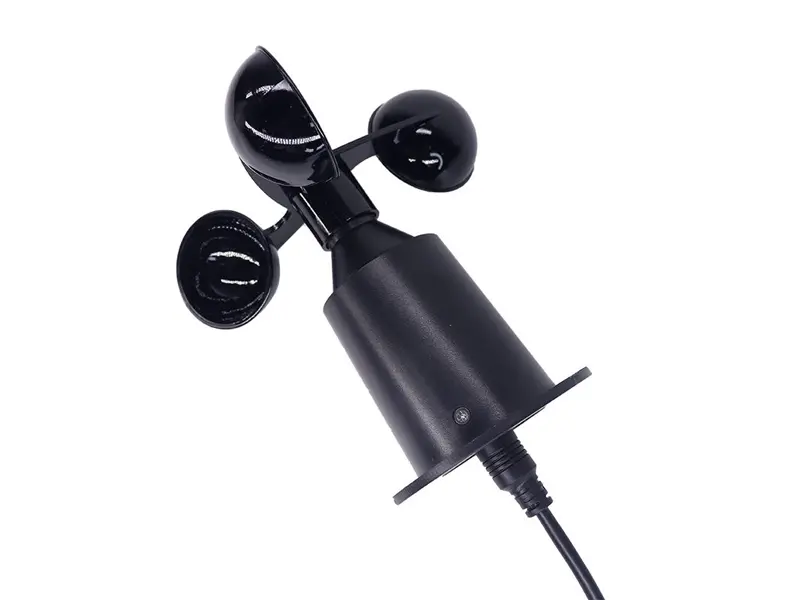

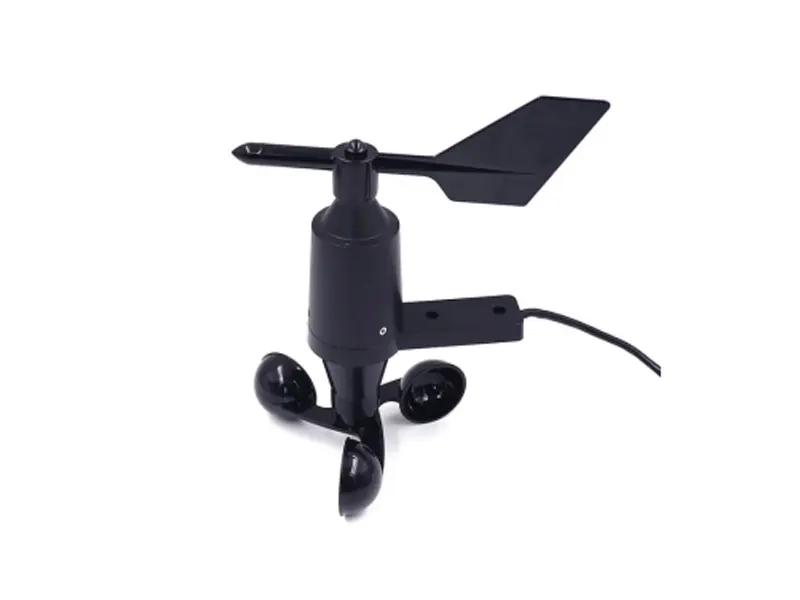
2. Propeller-type anemometer
Working Principle: Airflow drives the propeller to rotate, while simultaneously capturing wind direction through the directional mechanism.
Tính năng
- Accuracy: Moderately high
- Range: Low to medium wind speeds
- Response speed: Relatively fast
- Cost: Moderate
Đơn đăng ký
- HVAC systems
- Building ventilation testing
- Portable measurement
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Measures wind speed + direction | Sensitive to installation orientation |
| Performs well at low wind speeds | Mechanical structure requires maintenance |
| High portability | Not suitable for extreme environments |

3. Thermistor Anemometer
Working Principle: Calculates wind speed based on heat dissipation changes from heating elements.
Tính năng
- Accuracy: High (low wind speeds)
- Range: Low wind speeds
- Response Speed: Extremely fast
- Cost: Moderate
Đơn đăng ký
- Laboratories
- Cleanrooms
- Indoor airflow studies
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Ultra-high sensitivity | Susceptible to temperature and humidity |
| Extremely fast response | Extremely fast response |
| Ideal for light wind measurement | Requires frequent calibration |

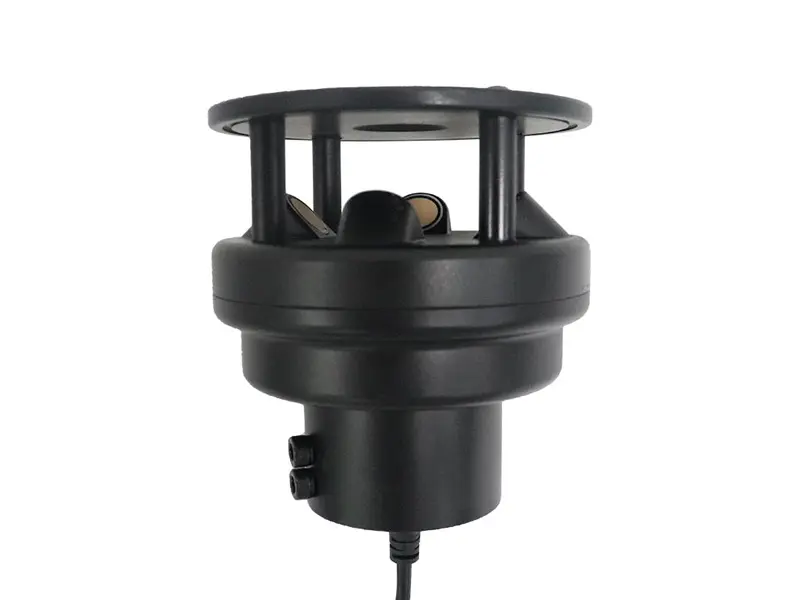
4. Ultrasonic Anemometer
Ultrasonic Anemometer Working Principle: Measures wind speed and direction by calculating the time difference of ultrasonic waves propagating through air.
Tính năng
- Accuracy: High
- Range: Wide
- Response Speed: Extremely Fast
- Durability: Exceptionally High
- Cost: Relatively High
Đơn đăng ký
- Wind Turbine Control
- Scientific Research and Observation
- Smart Weather Stations
- Marine and Extreme Environments
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| No mechanical wear | High initial cost |
| Maintenance-free, high stability | Demanding installation requirements |
| Suitable for harsh environments |

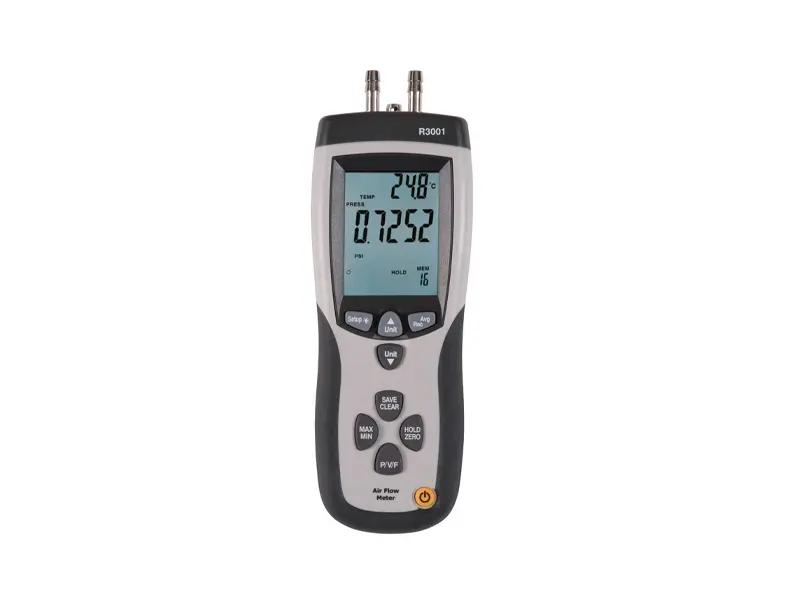
5. Pitot Tube Differential Pressure Anemometer
Working Principle: Calculates wind speed based on the difference between dynamic and static pressure.
Tính năng
- Accuracy: High (High Speed)
- Range: High Wind Speed
- Cost: Low to Medium
Đơn đăng ký
- Aerospace
- Wind Tunnel Testing
- Industrial Piping
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High accuracy at high wind speeds | Inaccurate at low wind speeds |
| Simple structure | Complex equipment |
| Mature industry | Not suitable for complex airflow patterns |

6. Laser Doppler Anemometer
Working Principle: Measures particle velocity in air using laser scattering frequency shift.
Tính năng
- Accuracy: Extremely high
- Contact Method: Non-contact
- Cost: Extremely high
Đơn đăng ký
- High-end research
- Fluid dynamics experiments
- Particle motion analysis
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Top-tier accuracy | Extremely high cost |
| No interference with airflow | Sensitive to installation location |
| Non-contact measurement | Non-industrial applications |

7. Wind Speed Direction Sensor
Wind Speed Direction Sensor Working Principle: Analyzes airflow movement through image recognition and AI algorithms.
Tính năng
- Accuracy: Under development
- Characteristics: Non-contact, intelligent
- Cost: Unstable
Đơn đăng ký
- Smart Cities
- Specialized scientific research experiments
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| No physical sensors | Standards not yet unified |
| Remote measurement possible | Susceptible to light interference |
| AI potential exists | Technology remains immature |

How to choose the right anemometer?
Selecting the right anemometer hinges not on price but on matching specific application requirements. First, clarify the measurement objectives: whether wind speed alone is needed or a combined wind speed and direction sensor is required. Next, consider the operating environment—whether it’s long-term field monitoring, industrial sites, or laboratory precision measurements—as these demand varying levels of waterproofing, dust resistance, corrosion resistance, and stability. Simultaneously, evaluate the required accuracy and response speed, distinguishing between industrial-grade monitoring and research-grade analysis. Finally, factor in the budget by weighing both the initial purchase cost and ongoing maintenance expenses. Only by balancing the application scenario, accuracy requirements, environmental conditions, and cost can you select the truly suitable anemometer.
Anemometer Industry Application Solution Recommendations
| Industry / Application | Recommended Solution | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Wind Power Industry | High-reliability ultrasonic anemometer | Combining regular calibration with redundant design |
| Giám sát môi trường | Durable cup anemometer + remote data transmission | Cost-effective and long-term stability |
| Building & HVAC | Propeller anemometer or thermal anemometer | Portable, with excellent low-wind-speed response |
| Scientific Research | Laser Doppler anemometer / high-precision ultrasonic anemometer | Ultimate Precision and Data Reliability |

Kết luận
Selecting an anemometer fundamentally involves balancing application scenarios, measurement accuracy, and long-term operational requirements. Price does not equate to performance; truly reliable data stems from equipment solutions that closely match operational conditions. Only through rational choices grounded in a thorough understanding of the usage environment, performance demands, and maintenance costs can anemometers deliver maximum value in practical applications, achieving stable, precise, and sustainable measurement objectives.